Salt Cloud¶
Configuration¶
Salt Cloud provides a powerful interface to interact with cloud hosts. This interface is tightly integrated with Salt, and new virtual machines are automatically connected to your Salt master after creation.
Since Salt Cloud is designed to be an automated system, most configuration is done using the following YAML configuration files:
/etc/salt/cloud: The main configuration file, contains global settings that apply to all cloud hosts. See Salt Cloud Configuration./etc/salt/cloud.providers.d/*.conf: Contains settings that configure a specific cloud host, such as credentials, region settings, and so on. Since configuration varies significantly between each cloud host, a separate file should be created for each cloud host. In Salt Cloud, a provider is synonymous with a cloud host (Amazon EC2, Google Compute Engine, Rackspace, and so on). See Provider Specifics./etc/salt/cloud.profiles.d/*.conf: Contains settings that define a specific VM type. A profile defines the systems specs and image, and any other settings that are specific to this VM type. Each specific VM type is called a profile, and multiple profiles can be defined in a profile file. Each profile references a parent provider that defines the cloud host in which the VM is created (the provider settings are in the provider configuration explained above). Based on your needs, you might define different profiles for web servers, database servers, and so on. See VM Profiles.
Configuration Inheritance¶
Configuration settings are inherited in order from the cloud config => providers => profile.
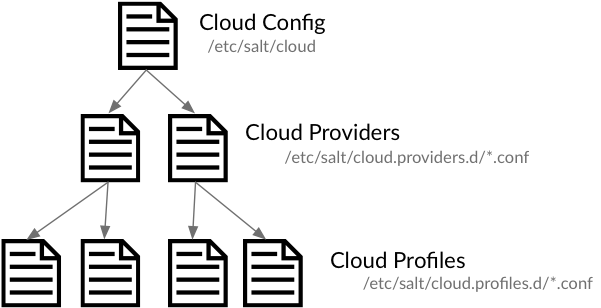
For example, if you wanted to use the same image for all virtual machines for a specific provider, the image name could be placed in the provider file. This value is inherited by all profiles that use that provider, but is overridden if a image name is defined in the profile.
Most configuration settings can be defined in any file, the main difference being how that setting is inherited.
QuickStart¶
The Salt Cloud Quickstart walks you through defining a provider, a VM profile, and shows you how to create virtual machines using Salt Cloud.
Note that if you installed Salt via Salt Bootstrap, it may not have
automatically installed salt-cloud for you. Use your distribution's package
manager to install the salt-cloud package from the same repo that you
used to install Salt. These repos will automatically be setup by Salt Bootstrap.
Alternatively, the -L option can be passed to the Salt Bootstrap script when
installing Salt. The -L option will install salt-cloud and the required
libcloud package.
Using Salt Cloud¶
Core Configuration¶
Windows Configuration¶
Cloud Provider Specifics¶
- Getting Started With Aliyun
- Getting Started With CloudStack
- Getting Started With DigitalOcean
- Getting Started With Dimension Data
- Getting Started With EC2
- Dependencies
- Configuration
- Access Credentials
- Windows Deploy Timeouts
- Key Pairs
- Security Groups
- IAM Profile
- Cloud Profiles
- Required Settings
- Optional Settings
- Modify EC2 Tags
- Rename EC2 Instances
- Rename on Destroy
- Listing Images
- EC2 Images
- show_image
- show_instance
- ebs_optimized
- del_root_vol_on_destroy
- del_all_vols_on_destroy
- EC2 Termination Protection
- Alternate Endpoint
- Volume Management
- Managing Key Pairs
- Launching instances into a VPC
- Getting Started With GoGrid
- Getting Started With Google Compute Engine
- Getting Started With HP Cloud
- Getting Started With Joyent
- Getting Started With Libvirt
- Getting Started With Linode
- Getting Started With LXC
- Getting Started With OneAndOne
- Getting Started With OpenNebula
- Getting Started With OpenStack
- Getting Started With Parallels
- Getting Started With ProfitBricks
- Getting Started With Proxmox
- Getting Started With Scaleway
- Getting Started With Saltify
- Getting Started With SoftLayer
- Getting Started With Tencent Cloud
- Getting Started With Vagrant
- Getting Started With Vexxhost
- Getting Started With Virtualbox
- Getting Started With VMware
- Getting Started With Xen
Miscellaneous Options¶
- Miscellaneous
- Deploy Script Arguments
- Selecting the File Transport
- Sync After Install
- Setting Up New Salt Masters
- Setting Up a Salt Syndic with Salt Cloud
- SSH Port
- Delete SSH Keys
- Keeping /tmp/ Files
- Hide Output From Minion Install
- Connection Timeout
- Salt Cloud Cache
- SSH Known Hosts
- SSH Agent
- File Map Upload
- Running Pre-Flight Commands
- Force Minion Config
Troubleshooting Steps¶
Extending Salt Cloud¶
- Adding Cloud Providers
- All Driver Modules
- Libcloud Based Modules
- Non-Libcloud Based Modules
- The
create()Function - The get_size() Function
- The get_image() Function
- The avail_locations() Function
- The avail_images() Function
- The avail_sizes() Function
- The script() Function
- The destroy() Function
- The list_nodes() Function
- The list_nodes_full() Function
- The list_nodes_select() Function
- The show_instance() Function
- The
- Actions and Functions
- Adding OS Support

